
Memory Management in Operating System
Welcome back! In the previous blog, we discussed CPU Scheduling Algorithms. Now, let’s dive into another fundamental responsibility of an operating system — Memory Management.
🧠 What is Memory Management?
Memory Management refers to the process by which an operating system handles and allocates computer memory to different programs and processes. It ensures efficient utilization of RAM and enables processes to execute smoothly without interfering with each other.
📂 Types of Memory in OS
- Primary Memory (RAM) – Fast, volatile memory where active processes are stored.
- Secondary Memory – Slower, permanent storage (like HDD/SSD).
- Cache Memory – Very fast memory close to the CPU, used for temporary data storage.
⚙️ Memory Allocation Techniques
1️⃣ Contiguous Memory Allocation
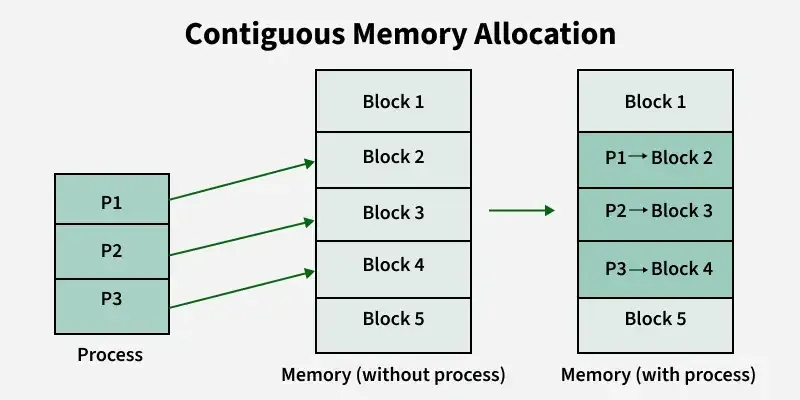
Each process is allocated a single block of memory. It’s simple but may lead to fragmentation.
- Fixed Partitioning: Memory is divided into fixed-size partitions.
- Variable Partitioning: Memory is allocated as per process size.
2️⃣ Paging

Paging is a memory management scheme that eliminates the need for contiguous allocation. The memory is divided into fixed-size blocks called pages (in logical memory) and frames (in physical memory).
Pages are mapped to frames using a Page Table.
3️⃣ Segmentation
In segmentation, the memory is divided into segments of variable sizes based on logical divisions like functions, arrays, or data structures. Each segment has a segment number and offset.
4️⃣ Virtual Memory
Virtual memory allows the execution of processes that may not be entirely in RAM. It uses disk space as an extension of RAM, enabling multitasking and large program execution.
📊 Comparison Table
| Technique | Contiguity | Fragmentation | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contiguous Allocation | Yes | High | Simple OS |
| Paging | No | Low | Modern OS |
| Segmentation | Yes | External | Modular Programming |
| Virtual Memory | Depends | Handled via paging | Multitasking |
📌 Real-Life Analogy
Memory Management is like a hotel manager assigning rooms to guests:
- Rooms = Memory blocks
- Guests = Processes
- Room service = OS manages who gets what and when
📝 Summary
- Memory management ensures smooth process execution.
- Paging and segmentation help in efficient memory allocation.
- Virtual memory extends RAM capabilities using disk space.
- Proper allocation improves system performance and multitasking.
